What You Need to Know about 5G for IoT

By now, we all know that the ‘I’ in IoT is for Internet. While understanding the internet’s past can give us insight into how that network could develop in the future, it can also show us where the second half of the acronym, the ‘oT’, fits in with that future. One way we forecast things is by looking at emerging technology, like 5G.
First of All, What is 5G?
Cell phone networks are systems of towers that transmit data and are delineated by generations which each transmit that data differently. The G means Generation, so 5G is the fifth generation of cell phone networks. It’s split into low, middle, and high band. It follows that 4G was the fourth generation, and so on back to 1G.
So what’s in a generation?
Each new generation of network will transmit data in a way different than the previous generations in order to give data transmission improvements in all three of the following respects:
1. Bigger Channels – This means higher data transmission speeds (e.g. faster file uploads and downloads)
2. Lower Latency – This means the network is more responsive (e.g. no lag on video chat)
3. More Connectivity – This means that more devices can be connected to the network at a given time. (e.g. Pokemon mobs won’t down the network)

5G, 5Ge, or 5Gs?
Some people have seen some ads saying that 5G is already here. They might have seen ads from network carriers saying that they have 5Gs or 5Ge ready now. Is this the real deal though?
Some of you may recall seeing signs and ads for 3.5G from some network carriers when 4G was coming out about 10 years ago. The carriers got in trouble for false advertising then, and it’s happening again, unfortunately. So it’s the same idea as before with 3.5G, 5Gs and 5Ge (or other things added to 5G) are not 5G, they’re 4G being disguised by the network carrier.
A Brief History of 5G
Knowing that the G means generation for these networks, let’s take a little refresher on what each generation gave us.
1. 1G: Analog Cellular – Those brick cell phones from the 1980s.
2. 2G: First generation of digital cellular technologies like CDMA, GSM, and TDMA – The indestructible Nokia everyone had in 2000.
3. 3G: Technologies such as EVDO, HSPA, and UMTS brought speeds from 200kbps to a few megabits per second – The first iPhone.
4. 4G: Technologies like WiMAX and LTE – The phones we use today.
5. 5G: Now scaling up to hundreds of megabits and even gigabit-level speeds – Few phones currently support 5G.
5G Will Be a Game-Changer
The generational improvement from 4G to 5G gives us bigger channels for more speed, lower latency for responsiveness, and connectivity giving access to more devices on the network. How are some industries looking to take advantage of these? As you can see in the image below, the possibilities are very open.
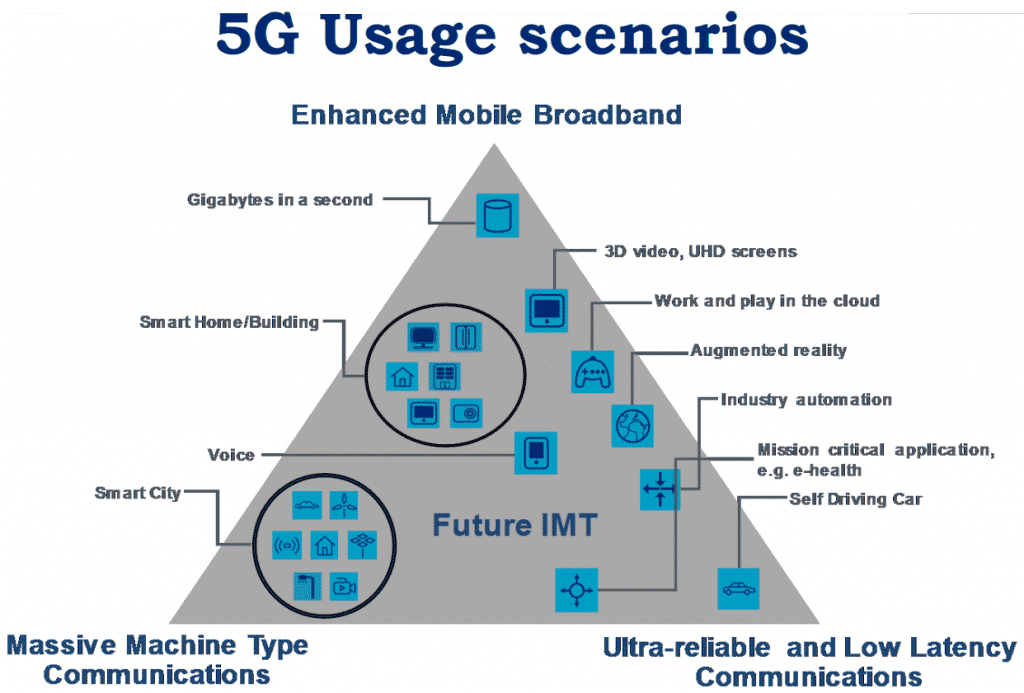
Some applications we foresee may rely more or less on one or all of those generational improvements and because it’s still emerging, a lot of it hasn’t even been conceived of yet. Imagine goods and packages that self-monitor and can report damages in real-time and being able to track them from the time they’re created in a factory, to the warehouse, all the way to your doorstep. This is just a glimpse into industrial IoT applications with 5G.
Consider the benefits that lie in wait for the auto industry, connected vehicles warning other cars of an accident that happened just a split second before. Thanks to the hyper-connectivity and low latency 5G is offering, perhaps UAV drones equipped with fire extinguishers will be on that same accident scene as above before the firetrucks.
Of course, self-driving cars being a majority on the streets will cut traffic in half. Or simply imagine being able to send a 10GB video to a friend in less than a minute. One thing is for certain, 5G is promising to deliver on so many things.
More smart home applications, more collaborative cloud based software that runs in real-time, this is great news for IoT and gives almost every industry a deeper well of application possibilities.
We’re essentially getting an internet upgrade!
When Will 5G Happen?
You want this now, I know and so do I. Adoption doesn’t happen overnight though. Each generation has generally taken about three to five years from their announced launch to full deployment. We expect 5G to be a similar deployment as 4G and the others. Network carriers are opening 5G networks in new markets more regularly now and we should see most of the larger metro areas with service by the end of 2021.
Your Impact on 5G & IoT
As 5G is just now rolling out, the opportunities, applications, and ideas that haven’t been thought of yet are sure to be many.
While finding reliable and proven solutions which add onto and give greater value to 5G networks can be a painstaking task to do alone, we will do the legwork for you. If you are looking to develop your own products to take advantage of 5G and are looking for suppliers to help, you can submit your project requirements here and we’ll match you with suitable suppliers.
For creators, being one module away from completing an IoT project that will use the utmost of 5G but not being able to find it is a frustrating roadblock so look here for 5G-ready IoT components and modules.
TechDesign is here to accelerate the IoT product development of hardware innovators like you. With 400+ suppliers and 700+ solutions, our professional project managers are able to help you find the most suitable solutions at any development stage. Hesitate no more, visit the TechDesign site today and submit a request!










